Longevity by Avea
Swiss-engineered solutions with 99% purity for a holistic longevity approach.
Every batch is rigorously third-party tested to ensure purity, safety, and effectiveness, giving you the confidence to prioritize your health with science-backed solutions.

Not sure where to start?
Supports natural collagen production
Promotes healthy glucose metabolism
Enhances cellular renewal and defense
Builds the base for optimising your health
Reduce inflammaging by balancing your gut microbiome and clearing aged cells
For healthy skin with a youthful radiance
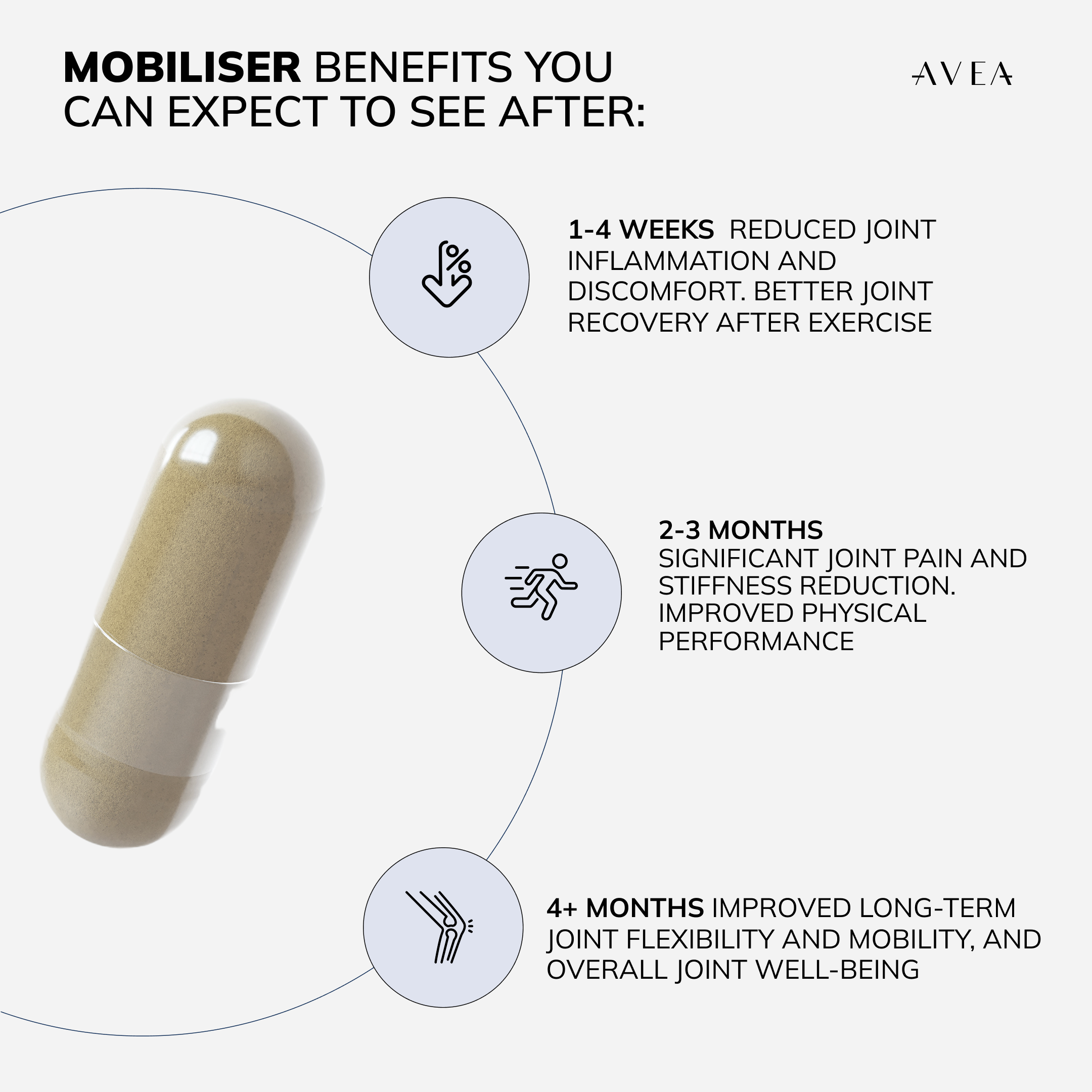
Boosts collagen for superior joint health and recovery.
Assess your NAD+ levels as well as key minerals' status